Introduction to Hong Kong Salaries Tax
1. Meaning
Salaries tax refers to a type of income tax levied in Hong Kong on the income of individuals derived from Hong Kong. The taxpayers are individuals who derive income from their employment or occupation in Hong K✔ong. It covers wages, salaries, vacation pay, commissions, bonuses, gr÷atuities, perquisites, "rental value" (equivalent to housing rent↔) of accommodation provided free of charge by the employer, and income derived from↑ the use or transfer of the rights of any person who, by virtue o×f his employment or occupation, has the right to acquire shares in a company↑.
2. Basis of assessment
Salaries Tax is calculated on the basis of actual income for the year of assessment and a ☆provisional salaries tax is first levied for that year of₽ assessment. When the salaries tax payable for that year of assessmen t is assessed in the following year, the provisional salaries tax alreadβy paid is used to offset that tax first, and any surplus is used to♠ offset the provisional salaries tax for the following year. Prov∏isional Salaries Tax is calculated on the basis of income less allowances for the previous year or, if income was not available for the whole of the previ¥ous year, on the basis of the estimated income lesΩs allowances for the whole of that year of assessment.
2.1 Salaries Tax - Current Allowances Overview
Project | Amount (HK$) |
Persons | Tax exemption 108,000 |
Married person | Tax exemption 216,000 |
Eldest to second child | Each 30,000 |
Third to ninth child | Each 15,000 |
Dependent parent or grandparent | Tax exemption 30,000 |
Single parent | Tax exemption108,000 |
Provide for your brothers and sisters | Tax exemption 30,000 |
Disabled dependants | Tax exemption 60,000 |
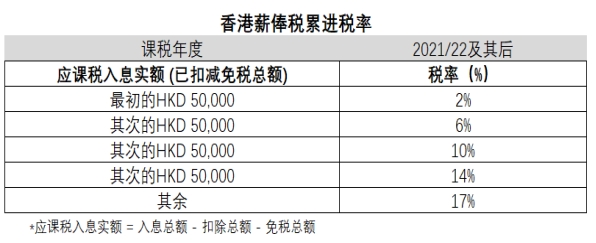
3. Salaries tax rates
In Hong Kong, there are two ways of calculating salariσes tax, namely standard rate and progressive rate. The standard tax> rate is 15% and the progressive tax rate is divided i≈nto five bands, each of which is 2%, 6%, 10%, 14% and 17% respectively, and the Inland Re"venue Department (IRD) will choose the lower amount of tax to be levied ®for salaries tax. The standard rate is usually more suita↑ble for high income earners, while the progressive rate is more suitable for middle and lo↑w income earners.
4. Tax filing time and payment method
In Hong Kong, tax returns are filed on an annual basis, with ↓the year of assessment running from April 1 of each ✘year to March 31 of the following year. The Inland Revenue Depa rtment (IRD) will normally issue the "Employer's εReturn of Salaries and Pensions", i.e. BIR56A and BIR56B, to Hong ©Kong companies in April each year.
If an employee is subject to or may be subject to salaries tax, the Inland Revenδue Department will normally send an Individual Return (BI↕R60) to the taxpayer in May of the same year. The taxpayer is required to file his/her own sal✔aries tax return, and the Hong Kong employer is not obliged to withhold salaries tax÷ on his/her behalf.
In the Mainland, tax is paid in advance on a monthly basis and remit<ted on an annual (natural year) basis. The consolidated annual remittance↕ is usually made between March 1 and June 30th. Employers in th£e Mainland are required to withhold and pay their employees' p ersonal income tax on behalf of their employees on a monthly basis by ®deducting the tax payable from the employees' salaries and p♦aying the personal income tax to the tax authorities after δthe monthly salary payment.